Common Terminology
Node - A Tree node is a component which may contain it’s own values, and references to other nodes Root - The root is the node at the beginning of the tree K - A number that specifies the maximum number of children any node may have in a k-ary tree. In a binary tree, k = 2. Left - A reference to one child node, in a binary tree Right - A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree Edge - The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node Leaf - A leaf is a node that does not have any children Height - The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf
Traversals
An important aspect of trees is how to traverse them. Traversing a tree allows us to search for a node, print out the contents of a tree, and much more! There are two categories of traversals when it comes to trees:
Depth First Breadth First
Binary Tree Vs K-ary Trees
In all of our examples, we’ve been using a Binary Tree. Trees can have any number of children per node, but Binary Trees restrict the number of children to two (hence our left and right children).
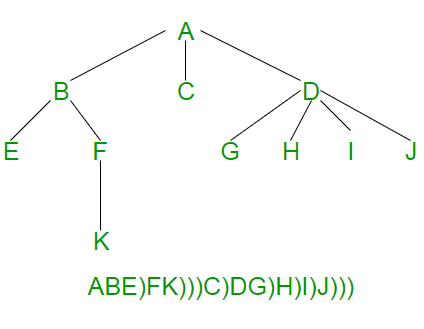
K-ary Trees
If Nodes are able have more than 2 child nodes, we call the tree that contains them a K-ary Tree. In this type of tree we use K to refer to the maximum number of children that each Node is able to have.
