Programming Problems
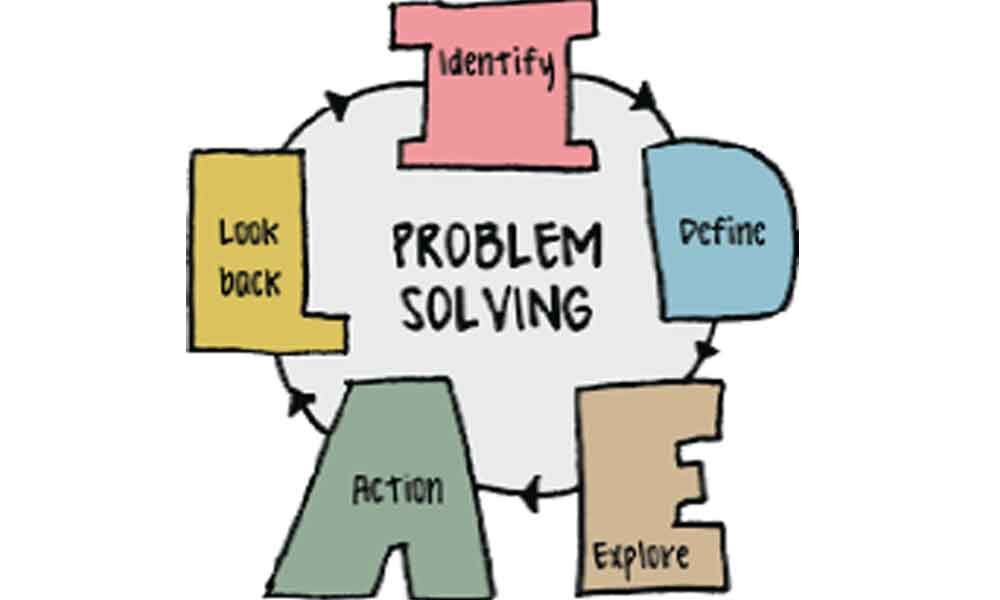
How to Solve Programming Problems
1-Read the problem completely twice. This is the single most important step ,You may even want to read the problem 3 or 4 times. You want to make sure you completely understand the problem.
2-A good test of this is whether or not you can explain the problem to someone else. 3-Solve the problem manually with 3 sets of sample data.
4-Optimize the manual steps.
5-Write the manual steps as comments or pseudo-code.
6-Replace the comments or pseudo-code with real code.
7-Optimize the real code.
How to think like a programmer
- Understand How to know when you understand a problem? When you can explain it in plain English. Plan Nothing can help you if you can’t write down the exact steps.
In programming, this means don’t start hacking straight away. Give your brain time to analyze the problem and process the information.
- Divide Pay attention. This is the most important step of all.
Do not try to solve one big problem. You will cry.
Instead, break it into sub-problems. These sub-problems are much easier to solve.
Then, solve each sub-problem one by one. Begin with the simplest. Simplest means you know the answer (or are closer to that answer).
After that, simplest means this sub-problem being solved doesn’t depend on others being solved.
Once you solved every sub-problem, connect the dots.
Connecting all your “sub-solutions” will give you the solution to the original problem. Congratulations!
Stuck? Debug: Go step by step through your solution trying to find where you went wrong. Programmers call this debugging (in fact, this is all a debugger does).
Reassess: Take a step back. Look at the problem from another perspective. Is there anything that can be abstracted to a more general approach?
Research: Ahh, good ol’ Google. You read that right. No matter what problem you have, someone has probably solved it. Find that person/ solution. In fact, do this even if you solved the problem! (You can learn a lot from other people’s solutions).
Practice
Practice. Practice. Practice. It’ll only be a matter of time before you recognize that “this problem could easily be solved with <insert concept here>.”
5 Whys, Getting to the Root of a Problem Quickly
When to Use a 5 Whys Analysis? You can use 5 Whys for troubleshooting, quality improvement, and problem solving, but it is most effective when used to resolve simple or moderately difficult problems.
How to Use the 5 Whys?
1-Assemble a Team, Gather together people who are familiar with the specifics of the problem, and with the process that you’re trying to fix.
2-Define the Problem, If you can, observe the problem in action. Discuss it with your team and write a brief, clear problem statement that you all agree on.
3-Ask the First “Why?”, Ask your team why the problem is occurring.
4-Ask “Why?” Four More Times, For each of the answers that you generated in Step 3, ask four further “whys” in succession. Each time, frame the question in response to the answer you’ve just recorded.
5-Know When to Stop, You’ll know that you’ve revealed the root cause of the problem when asking “why” produces no more useful responses, and you can go no further.
6-Now that you’ve identified at least one root cause, you need to discuss and agree on the counter-measures that will prevent the problem from recurring.
7-Keep a close watch on how effectively your counter-measures eliminate or minimize the initial problem.